New Tariffs by Trump: Global Impact on Inflation and Trade
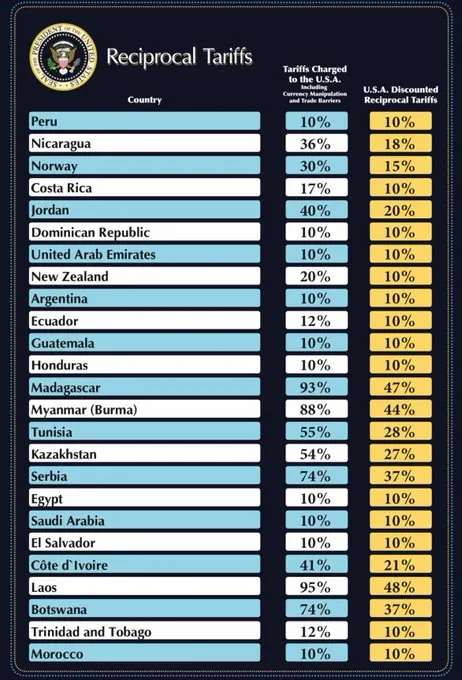
On April 2, 2025, President Donald Trump announced the implementation of sweeping new tariffs on imports from nearly all countries, aiming to reshape global trade dynamics and address perceived economic imbalances. The tariffs include a baseline 10% on all imports, with higher rates for specific countries: 20% for the European Union, 34% for China, and 25% on foreign-made vehicles.
The administration asserts that these measures will generate substantial revenue and encourage domestic consumption. However, economists and industry leaders have expressed concerns about potential negative impacts, including increased consumer prices, elevated inflation, and a slowdown in economic growth. For instance, estimates suggest that inflation could rise to 4.4% by year-end, potentially pushing unemployment to 5.5% in 2026.
International reactions have been swift and critical. Irish Prime Minister Micheál Martin condemned the tariffs as unjustified, warning of their damaging impact on jobs and inflation. The European Union is preparing countermeasures, emphasizing the importance of negotiation over confrontation.
While some sectors, such as oil, gas, and refined products, are exempt from these tariffs, the broad scope of the policy has raised fears of retaliatory measures from affected nations, potentially leading to a protracted trade war and prolonged economic uncertainty